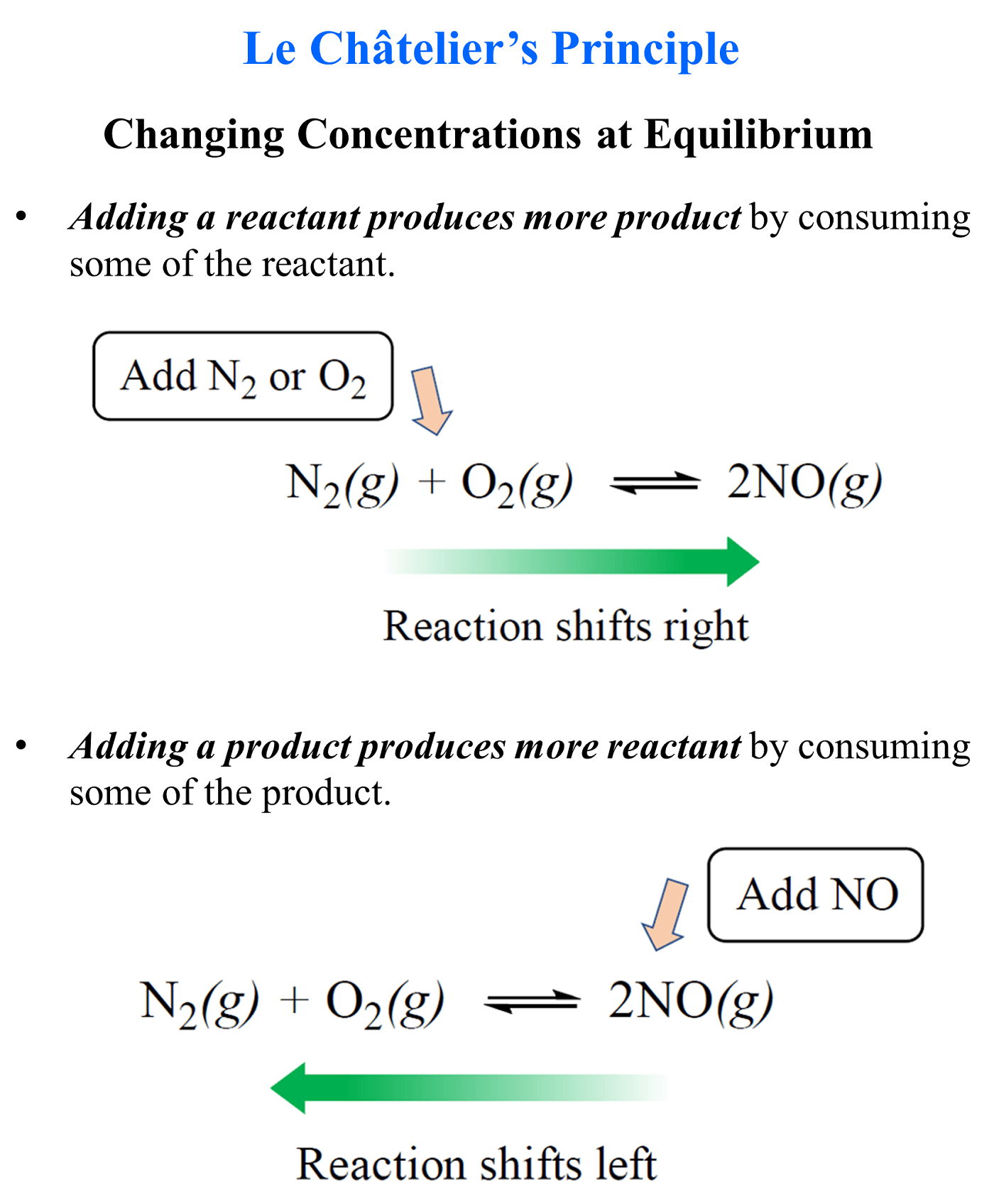In the previous post, we talked about Le Châtelier’s principle that helps evaluate the effect of changing the concentrations, volume, pressure, and temperature on the equilibrium. In short, you need to remember that if a system at equilibrium is disturbed, it will try to minimize the effect of external stress.
Practice
Consider the following equilibrium process
2SO3(g) ⇆ 2SO2(g) + O2(g) ΔH° = 2198 kJ/mol
How will the concentrations of SO2, O2, and SO3 be affected in each scenario?
(a) the temperature is increased
(b) the pressure is decreased by increasing the volume of the container
(c) the concentration of O2 is increased
(d) a is added catalyst
(e) an inert gas is added at a constant volume
Suppose you need to increase the amount of C3H6Cl2 produced in the following exothermic reaction:
C3H6(g) + Cl2(g) ⇆ C3H6Cl2(g)
Which of the following strategies will work once the reaction mixture reaches equilibrium?
a) decreasing the reaction volume
b) removing C3H6Cl2 from the reaction mixture as it forms
c) adding a catalyst
d) adding Cl2
e) increasing the temperature
Predict the shift in the equilibrium position that will occur for each of the following reactions at equilibrium when the volume of the reaction container is increased.
1) PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇆ PCl5(g)
2) 2NBr3(g) ⇆ N2(g) + 3Br2(g)
3) CO(g) + Cl2(g) ⇆ COCl2(g)
4) H2(g) + B2(g) ⇆ 2HBr(g)
5) MgCO3(s) ⇆ MgO(s) + CO2(g)
Consider the following equilibrium process for the commercial production of hydrogen:
CO(g) + H2O(g) ⇆ CO2(g) + H2(g) ΔH° = +42 kJ/mol
Predict the direction of the shift in equilibrium when
(a) the temperature is raised.
(b) more CO gas is added to the reaction mixture.
(c) some CO2 is removed from the mixture.
(d) the pressure on the gases is increased by changing the volume of the container.
(e) a catalyst is added to the reaction mixture
Consider this reaction at equilibrium:
N2 + O2(g) ⇆ 2NO(g)
Predict whether the reaction will shift left, shift right, or remain unchanged after each disturbance.
a) NO is added to the reaction mixture.
b) N2 is added to the reaction mixture.
c) NO is removed from the reaction mixture.
Check Also
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Equilibrium Constant
- Kp and Partial Pressure
- Kp and KcRelationship
- K Changes with Chemical Equation
- Equilibrium Constant K from Two Reactions
- Reaction Quotient – Q
- ICE Table – Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
- ICE Table Practice Problems
- Le Châtelier’s principle
- Chemical Equilibrium Practice Problems