This summary practice problem set covers the most common topics of chemical kinetics. You will find questions on the reaction rate, rate constant, rate law, integrated rate law, reaction half-life, and some more.
The links to the corresponding topics are given herein:
- Reaction Rate
- Rate Law and Reaction Order
- How to Determine the Reaction Order
- Integrated Rate Law
- The Half-Life of a Reaction
- Determining the Reaction Order Using Graphs
- Units of Rate Constant k
- How Are Integrated Rate Laws Obtained
- Activation Energy
- The Arrhenius Equation
- Chemical Kinetics Practice Problems
Practice
What are the three variables or factors that can affect the rate of reaction?
Show how the rate constant units for a zero, first, and second-order reaction can be derived if the concentrations are expressed in mol/L.
A tiny spark is enough to trigger a highly exothermic explosive reaction between natural gas/gasoline/hydrogen gas, etc.
Explain why a gas container does not explode without this spark.
Sketch a potential-energy diagram for an endothermic, elementary reaction
A + B → C + D
Indicate the reactants, products, the activation energy, the transition state, and the enthalpy change of the reaction.
Molecule A is transformed into molecule D through a multistep reaction. The energy diagram of the reaction is shown below:
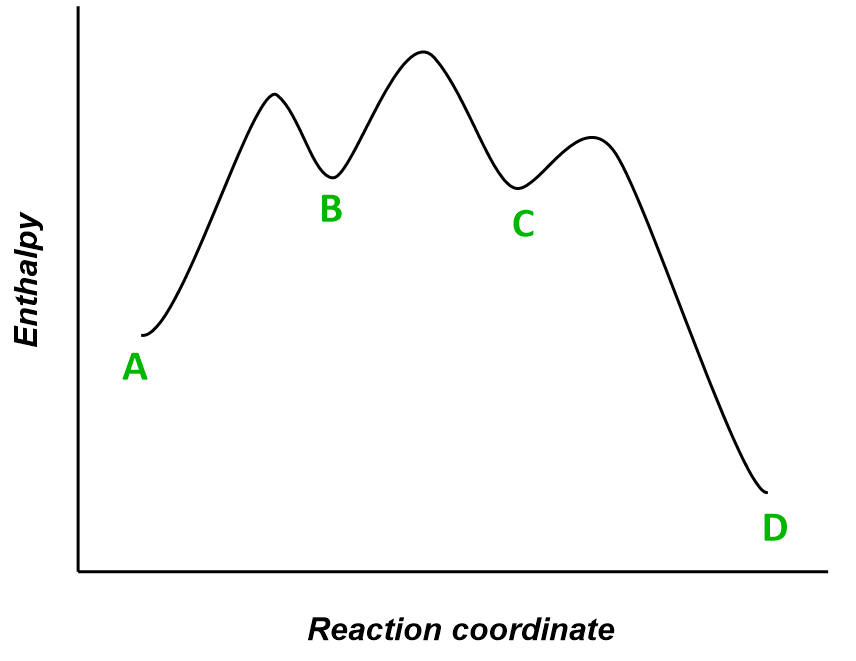
(a) How many intermediates are there in the reaction?
(b) How many transition states are there?
(c) Which is the fastest step in the reaction?
(d) Is the overall reaction exothermic or endothermic?
What is the difference between the rate of a chemical reaction and the rate constant?
Suppose it is determined that the following reaction is second order:
A + B → C
What are three different expressions for the rate law that can be applicable to the reaction? What does each rate law indicate about the mechanism of the reaction?
Consider the reactions:
a) 2NO(g) + 2H2(g) → N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
b) 4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Express the rate of the reaction in terms of the change in concentration of each of the reactants and products.
Consider the reaction of HCl forming H2 and Cl2 gases:
2HCl(g) → H2(g) + Cl2(g)
a) What is the average rate of the reaction during the first 45.0 s if the concentration of HCl dropped from 0.750 M to 0.430 M?
b) If the volume of the reaction is 2.50 L, what amount of Cl2 (in moles) will be formed during the first 20.0 s of the reaction?
Consider the Haber process for the synthesis of ammonia:
3H2(g) + N2(g) ⇆ 2NH3(g)
In the first 25.0 s of this reaction, the concentration of H2 dropped from 0.600 M to 0.512 M. Calculate the average rate of the reaction during this time interval.
At what rate is ammonia being formed in the previous example?
3H2(g) + N2(g) ⇆ 2NH3(g)
rate = 1.17 x 10-3 M/s
Consider the following decomposition reaction of SO3:
2SO3(g) → 2SO2(g) + O2(g)
During the first 75.0 s, the concentration of SO3 decreased from 0.265 mol/L to 0.189 mol/L. Determine the average rate of decomposition of SO3 during this time interval in mol/(L s).
Consider the reaction:
4NH3(g) + 5O2(g) → 4NO(g) + 6H2O(g)
Using the rate for the disappearance of NH3, fill out the missing data in the table.
| Δ[NH3]/Δt | Δ[O2]/Δt | Δ[NO]/Δt | Δ[H2O]/Δt | rate |
| -0.954 M/s |
Iron(II) ion is oxidized by hydrogen peroxide in an acidic solution.
2Fe2+ (aq) + H2O2(aq) + 2H+(aq) → 2Fe3+(aq) + 2H2O(l)
The rate law for the reaction is determined to be rate = k[H2O2 ][Fe2+]. The rate constant, at certain temperature, is 2.56 x 1024/M · s. Calculate the rate of the reaction at this temperature if [H2O2 ] = 0.48 M and [H2O2] = 0.070 M.
For the kinetics of the reaction
2NO(g) + Cl2(g) → 2NOCl(g)
The following data were obtained:
| Exp. | [NO] | [Cl2] | Initial rate, M/s |
| 1 | 0.25 | 0.35 | 0.68 |
| 2 | 0.25 | 0.70 | 1.36 |
| 3 | 0.50 | 0.70 | 2.72 |
a) What is reaction order in Cl2 and NO?
b) What is the rate law?
c) What is the value of the rate constant?
The date for the initial rate of the following reaction is listed in the table below:
A + B → C + D
| Exp. | [A] | [B] | Initial rate, M/s |
| 1 | 0.370 | 0.248 | 2.45 x 10-3 |
| 2 | 0.370 | 0.496 | 9.8 x 10-3 |
| 3 | 0.740 | 0.248 | 4.9 x 10-3 |
| 4 | 0.740 | 0.496 | 1.96 x 10-2 |
(a) What is the order of reaction with respect to A and to B?
(b) What is the overall reaction order?
(c) What is the value of the rate constant, k?
Consider the reaction
A(g) + B(g) ⇌ C(g)
The following data were obtained at a certain temperature:
| Exp. | [A] | [B] | Initial rate, M/s |
| 1 | 2.40 | 3.60 | 4.8 x 10-2 |
| 2 | 2.40 | 7.20 | 4.8 x 10-2 |
| 3 | 4.80 | 3.60 | 9.6 x 10-2 |
Using the data, determine the order of the reaction and calculate the rate constant:
Carbon dioxide, CO2, reacts with hydrogen to give methanol (CH3OH), and water.
CO2(g) + 3H2(g) ⇆ CH3OH(g) + H2O(g)
In a series of experiments, the following initial rates of disappearance of CO2 were obtained:
| Exp. | [CO2] | [H2] | Initial rate, M/s |
| 1 | 0.640 | 0.220 | 2.7 x 10-3 |
| 2 | 1.28 | 0.220 | 1.08 x 10-2 |
| 3 | 0.640 | 0.440 | 5.4 x 10-3 |
Determine the rate law and calculate the value of the rate constant for this reaction.
Integrated Rate Laws
Dinitrogen pentoxide, N2O5, decomposes when heated.
2N2O5(g) → 2N2O4(g) + O2(g) k = 3.4 x 10-6/s
What would be the concentration of N2O5 after running the reaction for 3.0 hr if the initial concentration of N2O5 was 0.0465 mol/L?
Hint, first determine the reaction order based on the units of k.
The following decomposition of phosphorus pentachloride (PCl5) was found to be a first-order reaction:
PCl5(g) → PCl3(g) + 6Cl2(g)
The half-life of the reaction is 48.0 s at a certain temperature. Calculate (a) the first-order rate constant for the reaction and (b) the time required for 75 percent of the phosphorus pentachloride to decompose.
The following data were collected for the decomposition reaction of hydrogen peroxide:
2H2O2(g) → 2H2O(g) + O2(g)
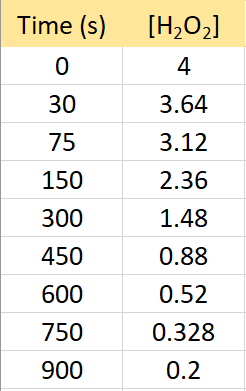
Determine rate law, the integrated rate law, and calculate the value of the rate constant.
In a laboratory experiment, the following kinetics data for the concentration of compound A versus time were collected:
A(g) → B(g) + C(g)
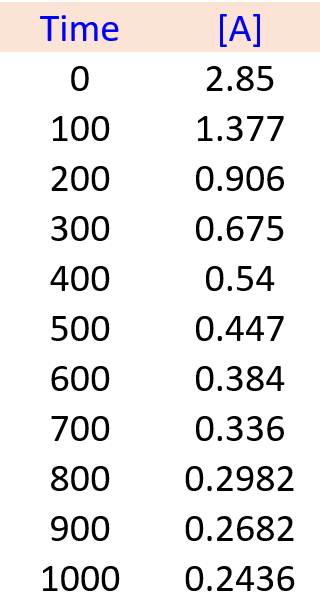
Determine the order of the reaction and the value of the rate constant. Predict the concentration of A at 450 s.
