Aufbau’s Principle, Hund’s Rule, and Pauli’s Exclusion Principle are rules for writing electron configurations, so go over the main principles of electron configurations if you need to before we start discussing them.
Aufbau’s Principle
Aufbau (German aufbauen, “to build up”) principle tells us that electrons fill the orbitals in the order of increasing their energy level. Remember, the main energy level is given by the principal quantum number, n, and it increases down the periodic table.
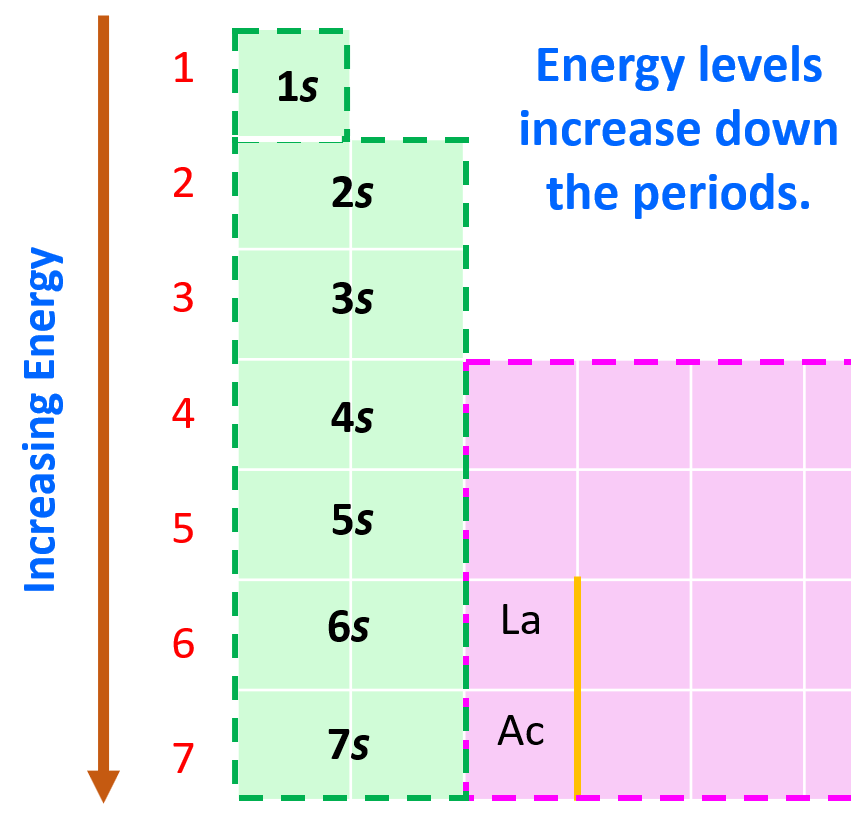
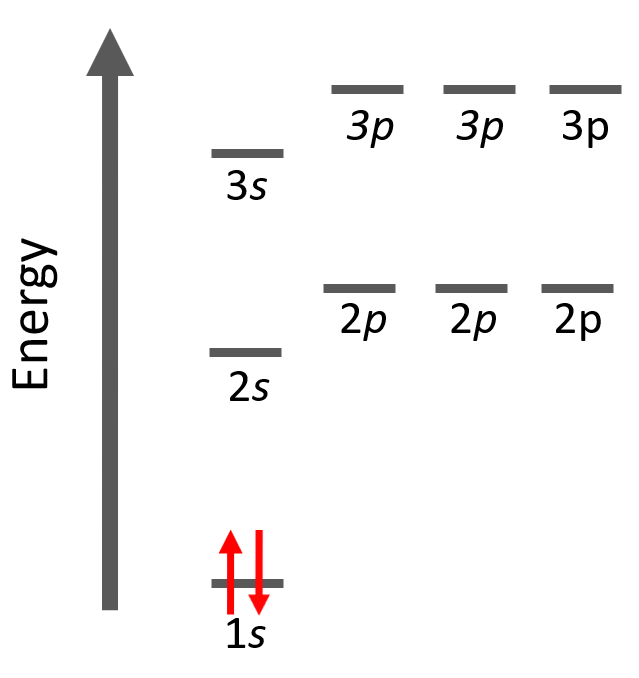
Here is a chart on the energy levels for up n = 4 which include the d sublevel:
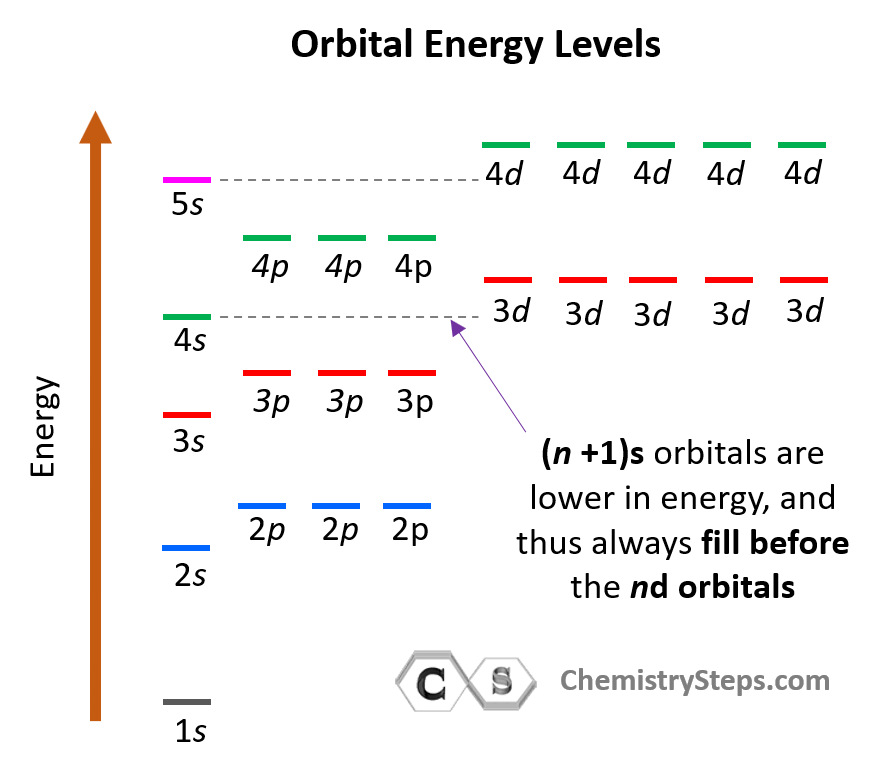
Consider also that within the same principal level, orbitals with a lower value of l have lower energy (E) and therefore, are filled first. So, for a given value of n:
E (s orbital) < E ( p orbital) < E (d orbital) < E ( f orbital)
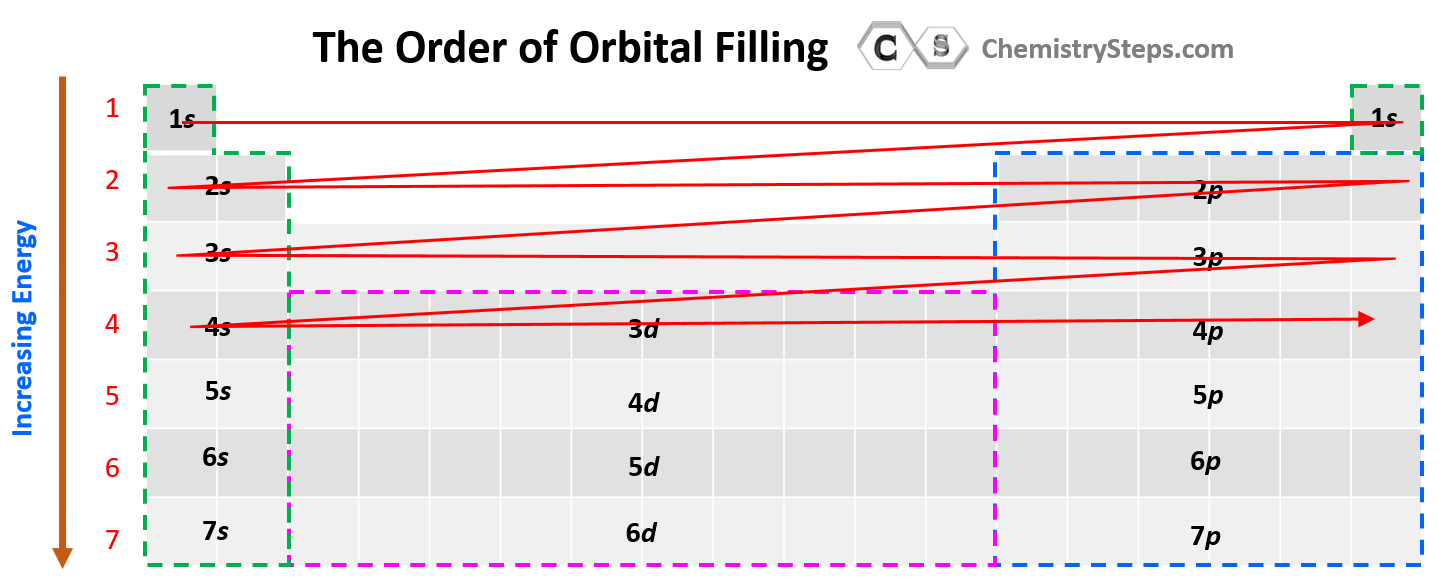
Notice that in the periodic table, it is opposite to what we show on the energy level diagram since the periods indicate the principal quantum number (n), which is the energy level, and they increase as we go down the periodic table. The general order for filling the electrons based on the energy levels and orbitals can be shown as in the picture below:
Let’s look at a few examples of following the Aufbau principle. For example, hydrogen has one electron and of course, we are going to put it in the 1s orbital it has the lowest energy.
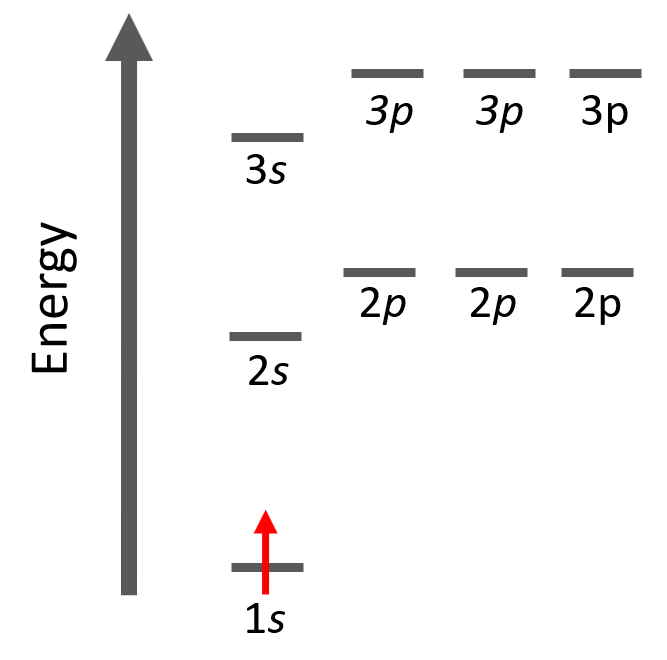
The electron configuration of hydrogen with orbital diagrams can be shown as:
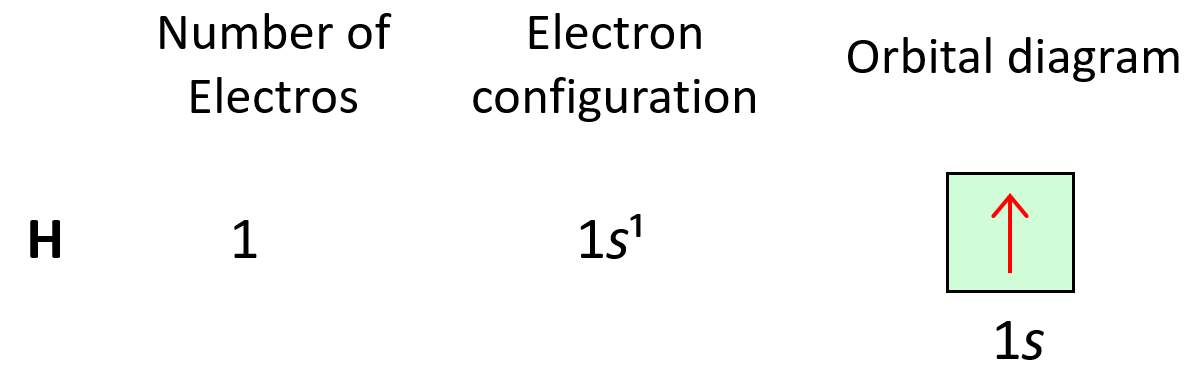
Next, we have helium, He – the second element in the periodic table. Remember, the number of electrons is equal to the atomic number as the number of electrons must be equal to the number of protons in a neutral atom. Therefore, He has two electrons and they both go to the 1s level because each orbital, regardless of if it is s, p, d, or f, can only accommodate a maximum of two electrons, and they wouldn’t go to the 2s level without filling the 1s:
The electron configuration of He with orbital diagrams can be shown as:

And this keeps going by adding one more electron to the next lowest energy orbital for every subsequent element in the periodic table.
Pauli’s Exclusion Principle
Notice that the arrow representing the second electron is pointing down, opposite to the first arrow which indicates that they must have opposite spins. This is according to the Pauli exclusion principle which states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same four quantum numbers. So, if the electrons are in the same orbital, they must have the same n, l, ml values, and therefore, the only one that can be different is the ms which is the spin of the electron shown by the position of the arrow.
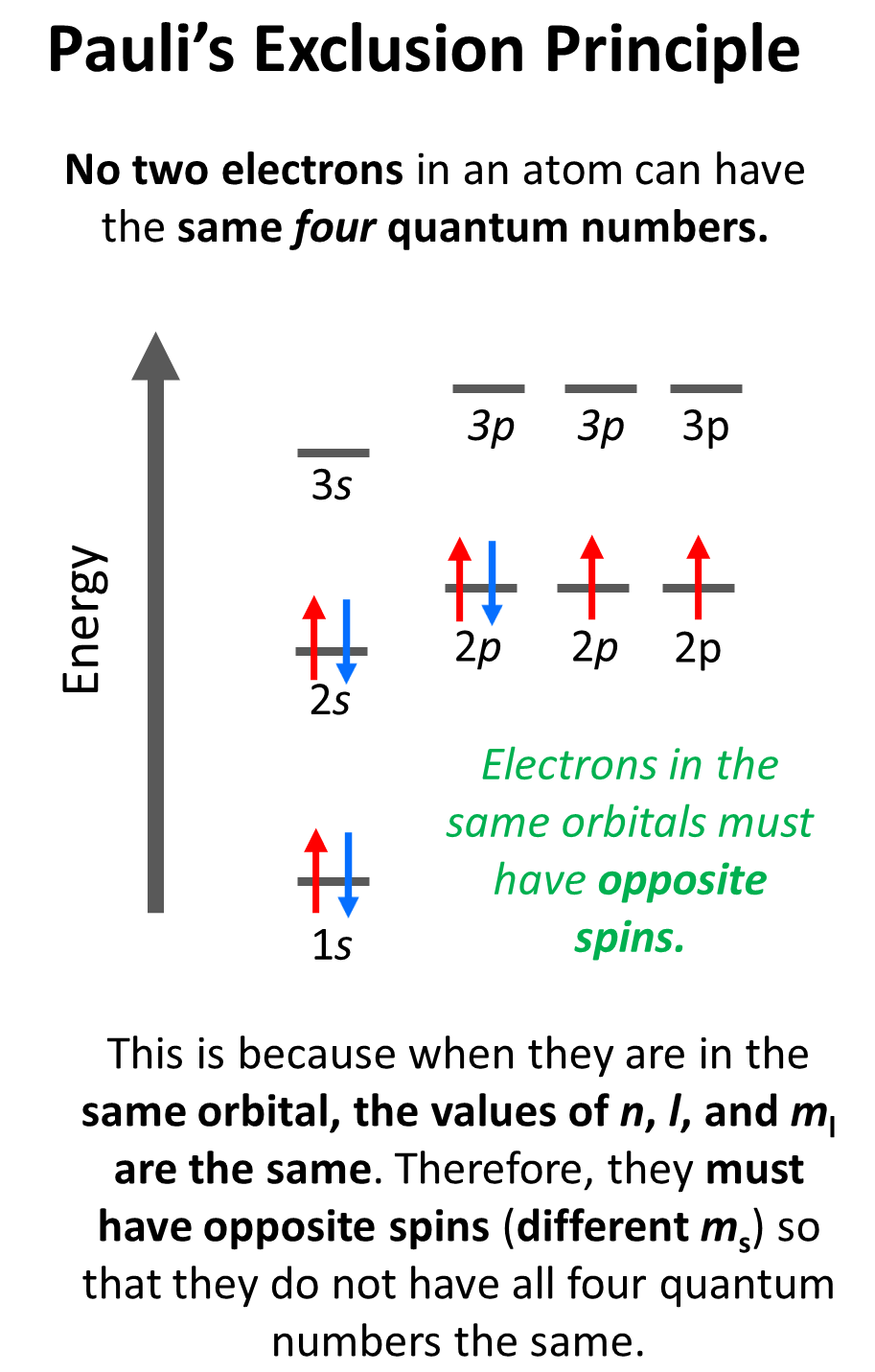
For example, for the electrons in a 2p orbital, n = 2, l = 1. and ml = –1, 0, or +1 (doesn’t matter which one because for the same orbital it will be identical). Therefore, the ms must be different (+1/2 or -1/2) so we don’t violate Pauli’s exclusion principle.
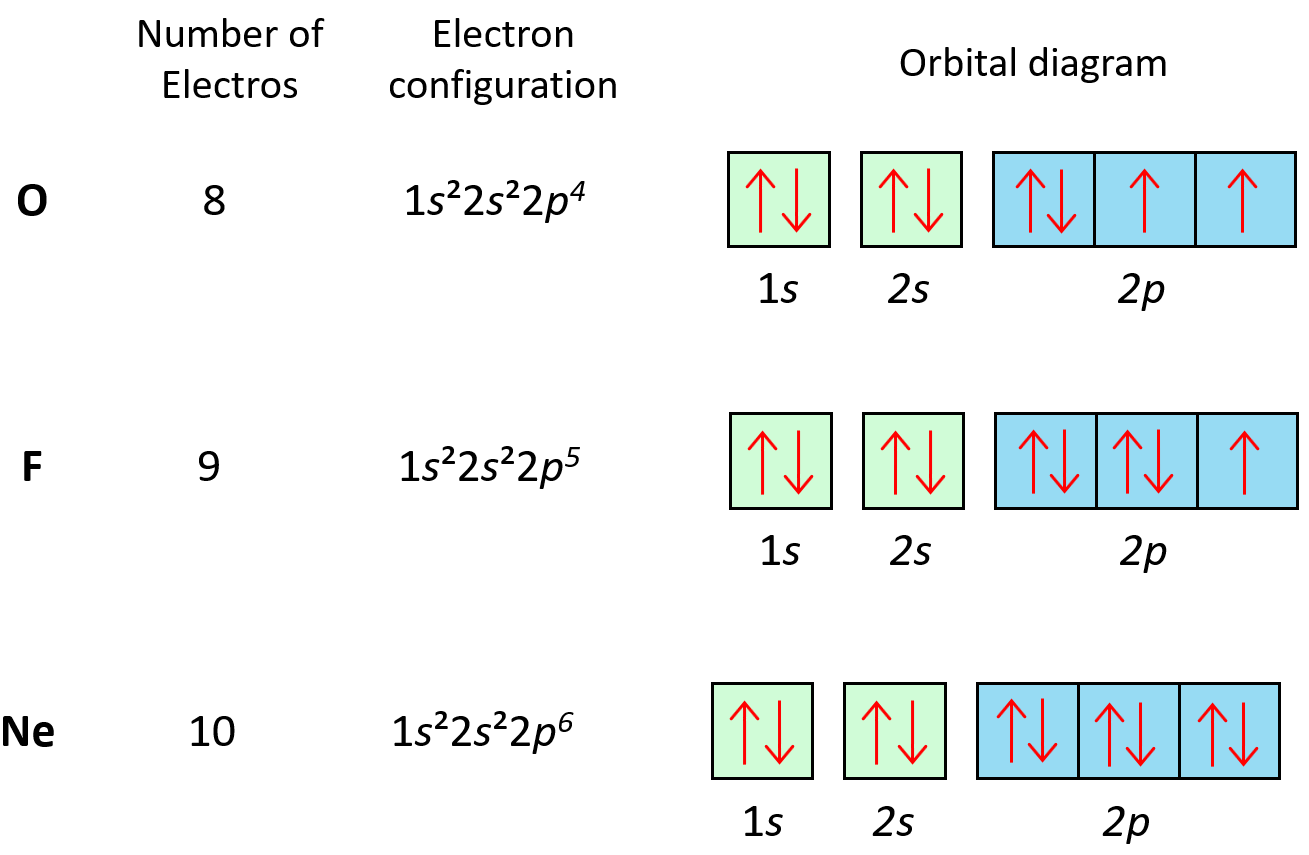
The principle applies to all the orbitals. For example, notice how the electrons in each p orbital of oxygen, fluorine, and neon are with opposite spins:
Hund’s Rule
To understand Hund’s tule, let’s first write the electron configuration of boron:
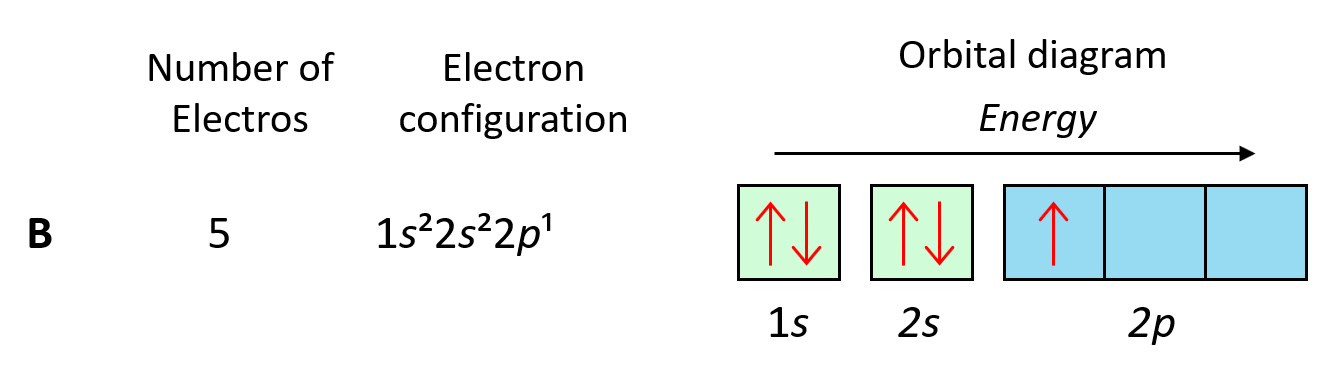
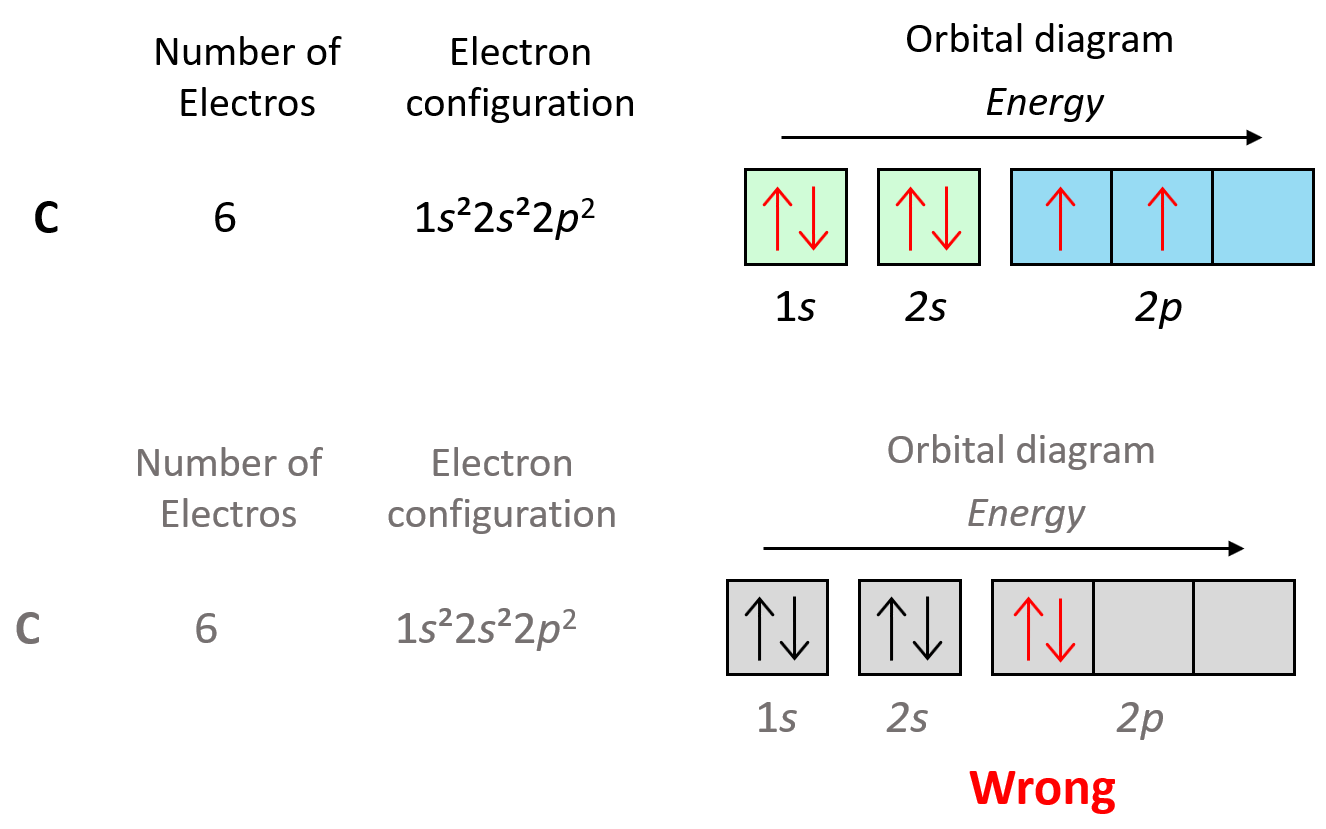
Now, the next electron, which indicates carbon, is going to have the option of pairing up with the one in the p orbital or going to the next empty p orbital. And it turns out that the electron goes to the next (empty) p orbital rather than fitting in with the other electron.
This is the Hund’s rule, which states that electrons will fill all the degenerate orbitals (equal in energy) with parallel spins (both arrows up or down) first before pairing up in one orbital. We can also formulate it as the lowest energy configuration for an atom is the one having the maximum number of unpaired electrons within the same energy sublevel.
Hund’s rule is another demonstration of the same principle which is the tendency to adopt the lowest energy state possible. There is a stronger repulsive interaction between two electrons in the same orbital compared to when they occupy separate orbitals of equal energy.
Let’s show the application of Hund’s rule in explaining the electron configuration of carbon:

Notice that placing the electron unpaired in the 3s orbital is also incorrect because, it is important to mention, that Hund’s rule applies to electrons in the same energy level. We are not going to place one of the electrons in the 3s orbital just for the sake of keeping a maximum number of unpaired electrons. It is energetically more favorable to have the electrons in the same lower sublevel rather than separating them by placing one in a higher energy level.
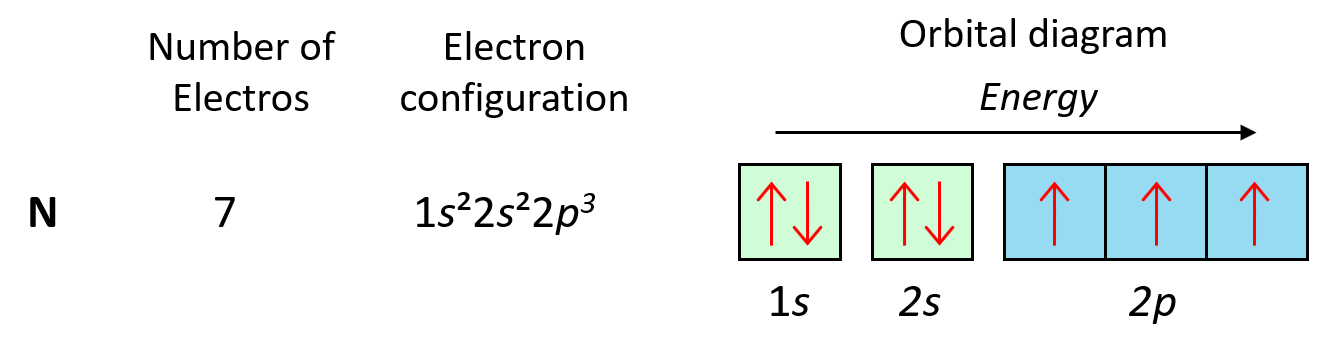
We can also demonstrate this using the orbital diagram of carbon:
As expected, the next element, nitrogen will place the additional electron in the 3rd p orbital which is empty in carbon.
Some exceptions occur in the electron configuration of d and f elements. First, recall that the (n +1)s orbitals always fill before the nd orbitals. For example, the 4s level fills before the 3d level, and therefore, the electron configuration of Ti is 1s²2s²2p⁶3s²3p⁶4s²3d² or, the condensed configuration which will be [Ar]4s²3d².
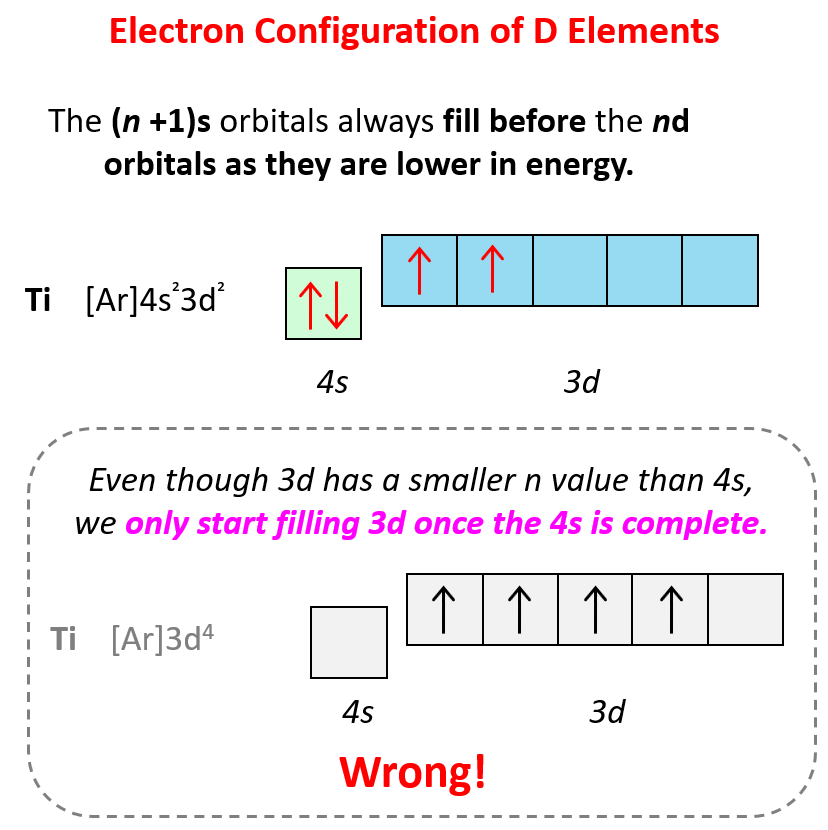
Sometimes having half-filled orbitals compensate for the energy gain associated with placing the electron in a higher-level orbital.
For example, unlike the expected [Ar]4s²3d4, the electron configuration of Cr is [Ar]4s13d5, and the reason for this is that the d orbital gets a half-filled configuration (remember d orbitals can have a maximum of 10 electrons). We can think of this as the electron jumping from the 4s level to the 3d level and compensating this energy uphill by a stabilization associated with half-filled orbitals:
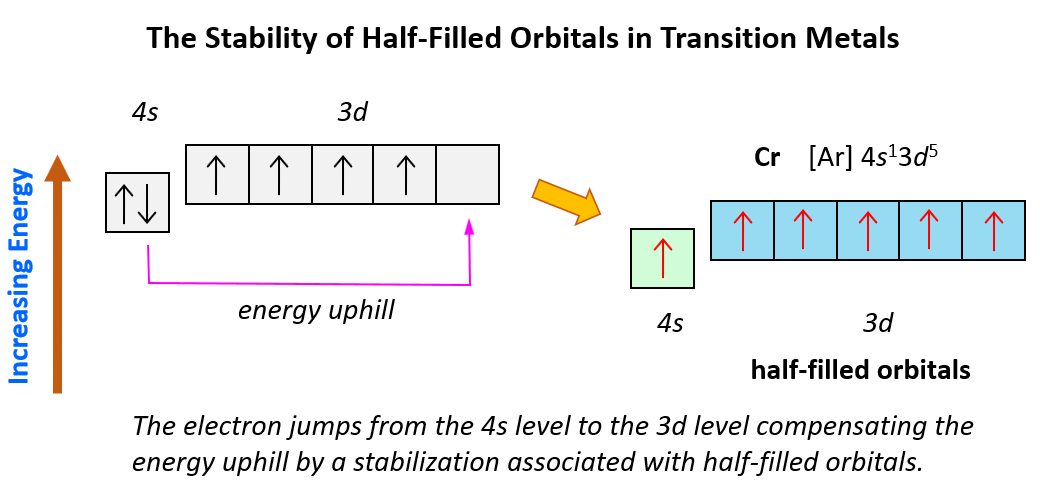
To summarize, remember that:
- The Aufbau principle is about filling the orbitals from lower to higher energy
- Pauli’s exclusion principle tells us to place the arrows of electrons in the same orbital in opposite directions.
- Hund’s rule tells us to place the electrons in different orbitals of the same energy sublevel (s, p, d, f) rather than pairing them up – more unpaired electrons is better.
Check this 95-question, Multiple-Choice Quiz on the Electronic Structure of Atoms including questions on properties of light such as wavelength, frequency, energy, quantum numbers, atomic orbitals, electron configurations, and more.
Check Also
- Atomic Orbitals
- Electron Configurations
- Electron Configurations of Ions
- Orbital Diagrams
- Hund’s Rule
- Pauli Exclusion Principle
- Quantum Numbers (n, l, ml, ms)
- Bohr Model of the Hydrogen Atom
- Rydberg Formula
- The Photoelectric Effect
- Calculating The Energy of a Photon
- Ionization Energy
- Electron Affinity
- Energy, Wavelength, and Frequency Practice Problems
Practice
What is the maximum number of electrons that can occupy one p orbital?
a.14
b. 2
c. 10
d.1
e. 6
The n = 2 shell can accommodate a maximum of ____ electrons.
A. 10
B. 8
C. 4
D. 6
E. 2
Which of the following is an incorrect orbital occupancy representation?
- 4d3
- 3d5
- 2s3
- 1s1
- 2p2
The maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in 3s subshell is
- 10
- 2
- 6
- 1
- 8
The following electron configuration is incorrect:
- 1s22s2
- 1s22s32p3
- 1s22s22p5
- 1s22s22p4
- 1s22s22p63s2
Which electron configuration represents an excited state of the indicated atom?
- He: 1s2
- Na: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p2 3s1
- P: 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p3
- N: 1s2 2s2 2p23s1
- Ne: 1s2 2s2 2p6
Which of the following represents the ground state electron configuration of a transition element?
- 1s22s22p63s23p5
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d104s1
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p4
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s2
- 1s22s22p3
Which of the following is the correct ground-state electron configuration of V is?
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d3
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d5
- 1s22s22p63s24s23d3
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d5
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d3
Which of the following represents a possible excited-state electron configuration for an iron atom?
- [Ar]3d74s2
- [Ar]3d64s2
- [Ar]3d74s1
- [Ar]3d64s1
- [Kr]3d74s1
Each of the following is an accurate representation of ground-state electron configuration except:
- Fe: [Ar]4s23d6.
- Ca: [Ar]4s2.
- Se: [Ar] 4s23d104p4.
- Ag: [Kr] 5s24d9.
- Ti: [Ar] 4s2 3d2
How many electrons, in total, are present in p orbitals in a ground-state nickel atom?
- 8
- 12
- 6
- 24
- 3
Which one of the following represents electron configuration of an excited carbon atom?
- 1s22s22p3
- 1s22s22p1
- 1s22s22p13s1
- 1s22s23s1
- 1s22s22p2
Which of the following ground-state electron configurations is incorrect?
- Cl: [Ne]3s23p5
- Ge: [Ar] 4s2 3d103p2
- Co: [Ar]4s23d7
- Rb: [Kr]5s1
- Mn: [Ar] 4s23d5
What is the ground-state electron configuration of chromium (Cr)?
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d104s24p64d105s25p4
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d5
- 1s22s22p63s23p63d10
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s23d4
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p63d6
What is the ground-state electron configuration of bromine (Br)?
- 1s2 2s2 2p6 3s2 3p6 4s1 3d10 4p5
- [Kr] 4s23s104p5
- [Ne] 3s2 3p5
- [Ar] 4s23d104p5
- 1s2 2s2 2p5 3s2 3p6 4s2 3d10 4p5
The ground state electron configuration of As is ________.
- 1s22s23s23p64s23d104p2
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p1
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104p3
- 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d104d3
- [Kr]4s23d104d3
Which of the following elements has the same valence-shell electron configuration as lithium?
- calcium.
- sulfur.
- potassium.
- magnesium.
- argon.
How many unpaired electrons are found in the d orbital of nickel.
- 4 electrons
- 3 electrons
- 2 electrons
- 8 electrons
- none of these
The ground-state electron configuration of the element ________ is [Kr]5s24d10
- Fe
- Cd
- Cr
- Mn
- Zn
The ground-state electron configuration of ________ is [Ar]4s23d7.
- Ti
- Co
- Fe
- Cr
- Cs
Chlorine has the following ground-state configuration:
- [He]3s23p2
- [Ne]3s23p5
- [He]2s22p5
- [Ne]2s22p3
- [He]3s23p5
What is the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in each d-subshell?
- 10
- 5
- 6
- 3
- 2
What noble gas core should be used when writing the condensed electron configuration of Strontium (Sr)?
- [Xe]
- [Kr]
- [Ne]
- [Ar]
- [He]
Electron Configuration of Ions
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of S2-?
A) [Ne]
B) [Ne]3s23p6
C) [Ne]3s23p4
D) [Ne]3s23p2
E) [Ne]4s2
A cation of +3 indicates that an element has
A) lost three neutrons.
B) lost three protons.
C) lost three electrons.
D) gained three protons.
E) gained three electrons.
Indicate the ground state electron configuration for Cl⁻.
A) 1s22s22p63s23p4
B) 1s22s22p63s23p5
C) 1s22s22p63s23p6
D) 1s22s22p63s13p6
E) 1s22s22p63s33p5
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Ba2+ ?
A) [Kr]5s24d105p66s2
B) [Kr]5s24d105p6
C) [Kr]5s24d105p65d2
D) [Kr]5s25p6
E) [Kr]5s24d105p66s2
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Ti2⁺.
A) [Ar]3d4
B) [Ar]3d2
C) [Ar]4s2
D) [Ar]4s23d4
E) [Ar]4s23d2
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Zn2⁺?
A) [Ar]4s23d6
B) [Ar]3d10
C) [Ar]4s23d8
D) [Ar]3d8
E) [Ar]
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Cr3⁺?
A) [Ar]
B) [Ar]4s13d2
C) [Ar]3d3
D) [Ar]4s23d1
E) [Ar]4s23d7
How many valence electrons are present in the azide (N3-) ion?
A) 3
B) 5
C) 8
D) 7
E) 2
Ca2+ has the following ground state electron configuration:
A) 1s22s22p6
B) 1s22s22p63s2
C) 1s22s22p63s23p2
D) 1s22s22p63s23p64s23d2
E) 1s22s22p63s23p6
Rb+ has the following ground state electron configuration:
A) [Kr]5s24d6
B) [Kr]4s2
C) [Ar]4s24p4
D) [Kr]5s1
E) [Ar]4s23d104p6
Which of the following is the ground state electron configuration of Fe3⁺?
A) [Ar]3d5
B) [Ar]4s13d3
C) [Ar]
D) [Ar]4s23d9
E) [Ar]4s23d1
The correct ground state electron configuration for Br– is:
A) [Ar]4s23d104p6
B) [Ar]4s23d104p3
C) [Ar]4s23d84p6
D) [Ar]4s23d104p5
E) [Ar]4s24p6
How many electrons are present in the ground state of Mg2+ ion?
A) 2
B) 6
C) 10
D) 8
E) 12

