In the previous post, we talked about ICE tables which we use for determining the equilibrium concentrations based on the equilibrium constant, reaction quotient, and the initial concentrations of the reactants and products.
Below are some additional practice examples on the concept of ICE tables and equilibrium concentrations.
Practice
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 600 oC is determined to be Kc = 0.495:
H2O(g) + CO(g) ⇆ H2(g) + CO2(g)
Calculate the number of H2 moles that are present at equilibrium if a mixture of 0.400 mole CO and 0.500 mole H2O is heated to 600°C in a 10.0-L container.
The equilibrium constant Kc for the following reaction at 800°C is 3.74 x 105
H2(g) + I2(g) ⇆ 2HI(g)
If 6.25 moles of HI were initially added to a 15.0-L empty vessel, what would the concentrations of H2, I2, and HI be at equilibrium.
The equilibrium constant for the following reaction at 700 K is Kp = 6.7 x 10-3
CO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇆ CH3OH(g)
A reaction mixture contains 0.248 atm of H2, 0.085 atm of CO, and 0.598 atm of CH3OH. Is the reaction mixture at equilibrium? If not, in what direction will the reaction proceed?
For the reaction shown below, Kc = 0.654 at 600 K.
N2O4(g) ⇆ 2NO2(g)
If initially, 0.0600 M of N2O4 are present in the reaction vessel, what are the equilibrium concentrations of the gases at 600 K?
For the reaction shown below, Kc = 255 at 800 K.
PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) ⇆ PCl5(g)
If a reaction mixture initially contains 0.3500 M PCl3 and 0.375 M Cl2 at 800 K, what are the equilibrium concentrations of all the species in the mixture?
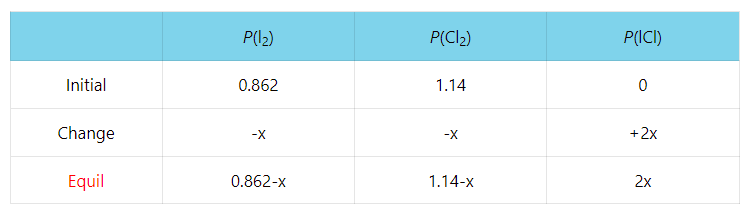
Consider the following reaction characterized with Kp = 2.34 x 10-4 at 250 K:
I2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇆ 2ICl(g)
A reaction mixture initially contains I2 with partial pressure of 655 torr and Cl2 with partial pressure of 864 torr at 250 K. Calculate the equilibrium partial pressure of ICl.
Consider the following equilibrium:
2NO(g) + 2H2(g) ⇆ N2(g) + 2H2O(g)
Initially, there are 0.15 moles of NO and 0.25 moles of H2, in a 10.0-L container. If there are 0.056 moles of NO at equilibrium, how many moles of N2 are present at equilibrium?
Check Also
- Chemical Equilibrium
- Equilibrium Constant
- Kpand Partial Pressure
- Kp and KcRelationship
- K Changes with Chemical Equation
- Equilibrium Constant K from Two Reactions
- Reaction Quotient – Q
- ICE Table – Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
- ICE Table Practice Problems
- Le Châtelier’s principle
- Le Châtelier’s principle Practice Problems
- Chemical Equilibrium Practice Problems